Modeling
Model-Driven Architecture (MDA) and Model-Driven Development (MDD)
Definition
Model-Driven Architecture (MDA) is a software design and development approach that focuses on creating and utilizing models to represent different aspects of a system. It is an initiative by the Object Management Group (OMG) to promote a standardized way of developing software systems using models as primary artifacts.
Key Features
Entity Data Modeler: codbex provides a powerful Entity Data Modeler tool that allows users to visually design data models for their applications. Users can define entities, attributes, relationships, and constraints using an intuitive graphical interface. The Entity Data Modeler simplifies the process of designing and managing complex data structures, enabling developers to focus on higher-level application logic.
Generation and Application Templates: codbex offers built-in generation capabilities and a library of application templates to accelerate development. Users can generate application code, including database schema, backend logic, and frontend components, based on predefined templates and configurations. This reduces the time and effort required to build new applications, ensuring consistency and quality across projects.
Predefined Reference and Master Data Modules: The codbex platform includes a repository of predefined reference and master data modules that cover common business domains and industries. These modules contain standard data structures, rules, and workflows that can be easily integrated into applications. By leveraging these predefined modules, developers can expedite development and ensure compliance with industry standards and best practices.
Application Building Blocks Modules: codbex provides a library of reusable application building blocks, such as authentication, authorization, user management, and reporting modules. These building blocks encapsulate common functionality and business logic, allowing developers to quickly assemble custom applications from pre-existing components. This modular approach promotes code reuse, simplifies maintenance, and accelerates time-to-market for new applications.
Key Concepts
Platform-Independent Model (PIM):
- A PIM represents the system's functionality independently of any specific technology or platform. It is a high-level abstraction that captures the essential aspects of the system.
Platform-Specific Model (PSM):
- A PSM represents the system's functionality in terms of a specific technology or platform. It serves as a bridge between the high-level abstraction of the PIM and the concrete implementation details.
Transformation:
- Transformation processes are used to convert models from a higher abstraction level (PIM) to a lower one (PSM). This process involves applying rules and templates to generate code or artifacts for a particular platform.
Code Generation:
- Automated code generation is a key aspect of MDA. It involves transforming models into executable code for a specific technology stack. This can significantly reduce the manual coding effort and improve consistency.
Reusability:
- MDA encourages the reuse of models and transformations across projects, promoting consistency and efficiency in software development.
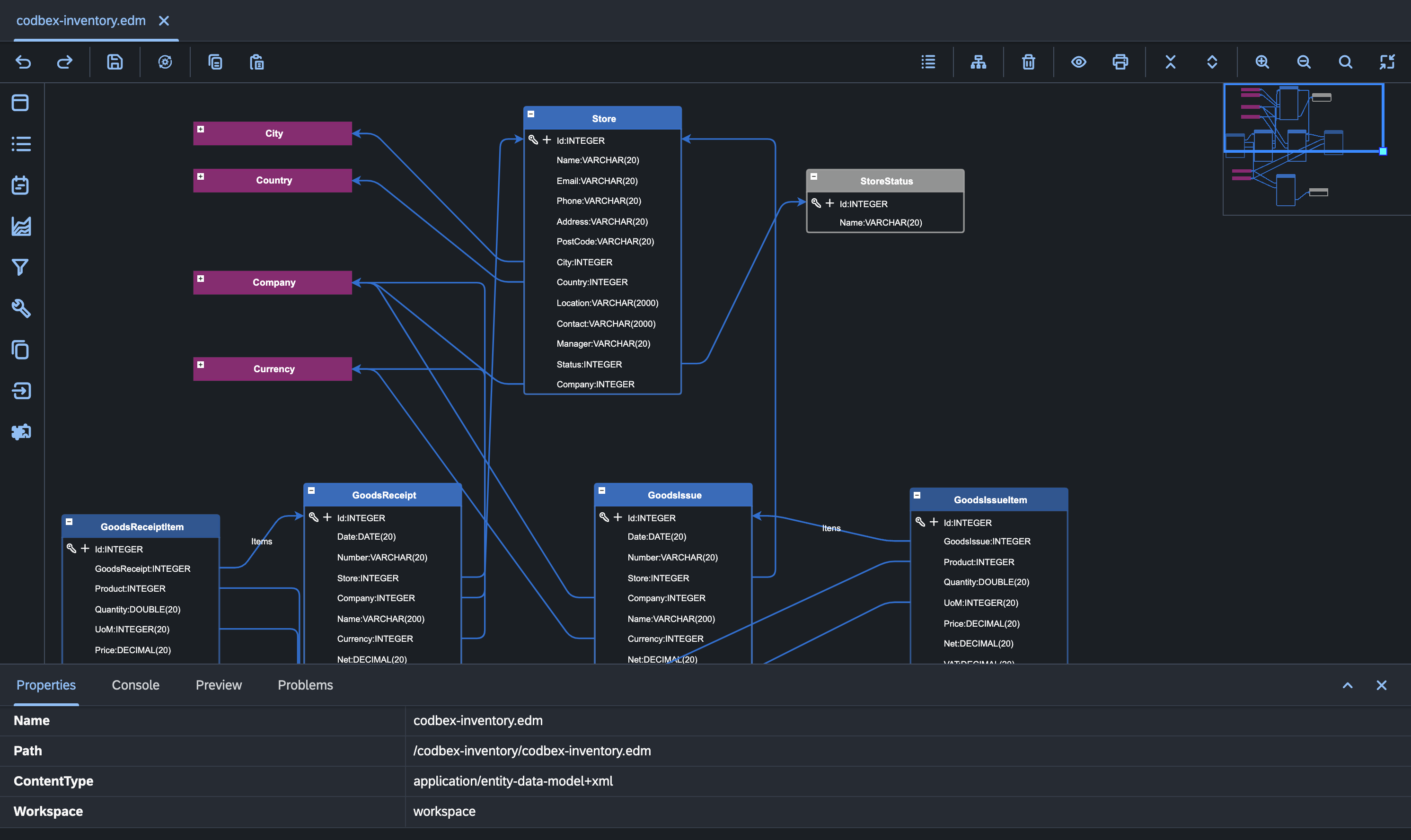
Entity Data Modeler (EDM)
Overview
The Entity Data Modeler (EDM) is a component within the MDA framework that focuses on designing the data model of an application. It allows developers to graphically create, visualize, and modify domain objects (entities) and their relationships.
Key Features
Graphical Modeling:
- EDM provides a visual environment for creating domain objects and defining their attributes. Developers can design the data model by dragging and dropping entities, specifying properties, and establishing relationships.
Properties for Various Aspects:
- Developers can assign properties to entities for different purposes, such as defining database-related settings (e.g., table names, constraints), user interface attributes, security configurations, and other relevant metadata.
Relationships and Dependencies:
- EDM allows users to model relationships between entities, specifying associations, cardinalities, and dependencies. This ensures a clear representation of how different parts of the system are connected.
Code Generation Templates:
- Predefined templates and rules for code generation are associated with the EDM. These templates guide the transformation process, automatically generating code based on the graphical models created by developers.
Consistency and Maintainability:
- By centralizing the data model in a visual environment, EDM promotes consistency and maintainability. Changes made to the model are reflected in the generated code, reducing the chances of inconsistencies.
Template Customization:
- Advanced users can customize code generation templates to tailor the generated code to specific project requirements. This flexibility allows developers to adapt the generated artifacts to the unique needs of their applications.
Workflow
Modeling:
- Use the graphical interface to create entities, define attributes, and establish relationships.
Property Assignment:
- Assign properties to entities for database, user interface, security, and other configurations.
Validation:
- Validate the model to ensure it adheres to predefined rules and constraints.
Code Generation:
- Trigger the code generation process, transforming the graphical model into executable code.
Application Development:
- Build and extend the generated code to implement business logic and additional functionalities.
Benefits
Efficiency:
- EDM accelerates the development process by providing a visual and centralized way to design the data model.
Consistency:
- Models and generated code remain consistent, reducing the likelihood of errors caused by manual changes.
Adaptability:
- Developers can adapt the generated code to meet specific project requirements while leveraging predefined templates.
Collaboration:
- Teams can collaborate more effectively by working with a common visual representation of the data model.
In conclusion, the Entity Data Modeler within the Model-Driven Architecture framework empowers developers to design robust data models visually and efficiently generate code based on those models. This approach enhances consistency, maintainability, and collaboration in software development projects.